ISRO successfully performed a key manoeuvre of its solar mission Aditya-L1
Tue 19 Sep 2023, 10:54:58
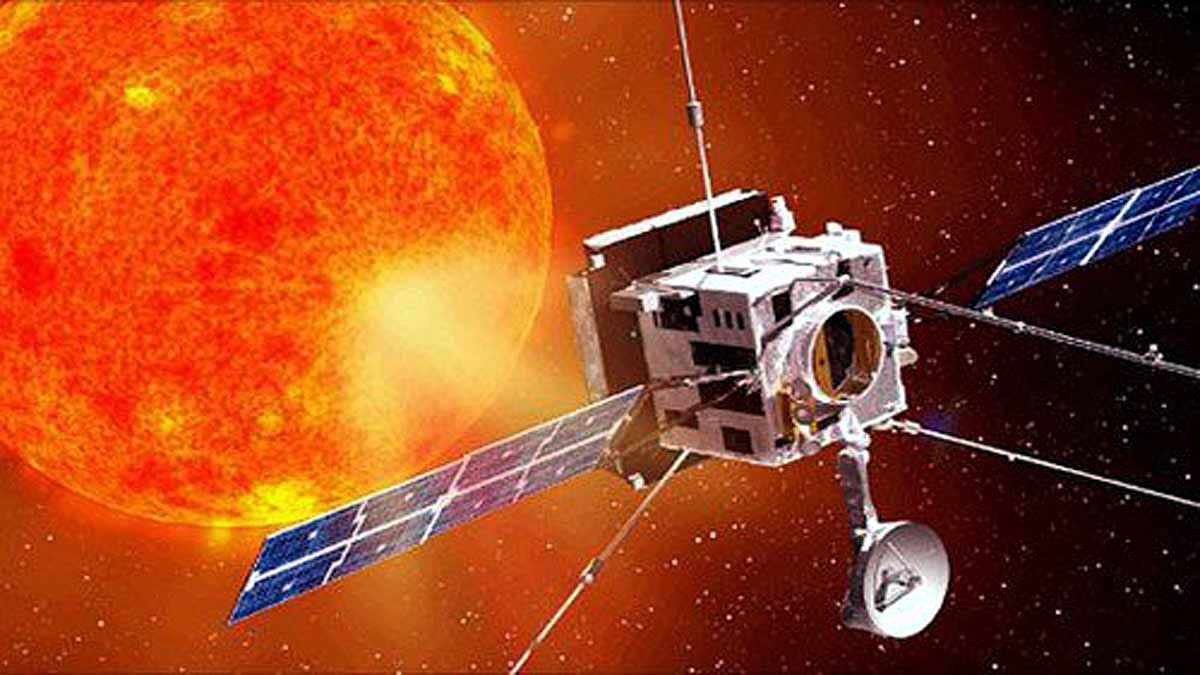
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) yesterday successfully performed a key manoeuvre of its solar mission Aditya-L1. The Trans-Lagrangian Point 1 Insertion manoeuvre marks the beginning of the spacecraft's about 110-day trajectory to the destination around the L1 Lagrange point, a balanced gravitational location between the Earth and the Sun.
The spacecraft is now on a trajectory that will take it to the Sun-Earth L1 point. It will be injected into an orbit around L1 through a maneuver after about 110 days," ISRO said in a post on X (formerly Twitter).
Aditya-L1
is the first Indian space-based observatory to study the Sun from a halo orbit around first Sun-Earth Lagrangian point (L1), located roughly 1.5 million km from earth. The Sun is a giant sphere of gas, and Aditya-L1 will study the outer atmosphere of the Sun.
is the first Indian space-based observatory to study the Sun from a halo orbit around first Sun-Earth Lagrangian point (L1), located roughly 1.5 million km from earth. The Sun is a giant sphere of gas, and Aditya-L1 will study the outer atmosphere of the Sun.
According to ISRO, a spacecraft placed in the halo orbit around the L1 point has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation /eclipses. This will provide a greater advantage of observing the solar activities and its effect on space weather in real-time.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from National
Most viewed from World
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Should there be an India-Pakistan cricket match or not?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2026 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.




































.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


