PM Modi warns against antibiotics, doctor says the concern is real
Tue 30 Dec 2025, 01:06:43
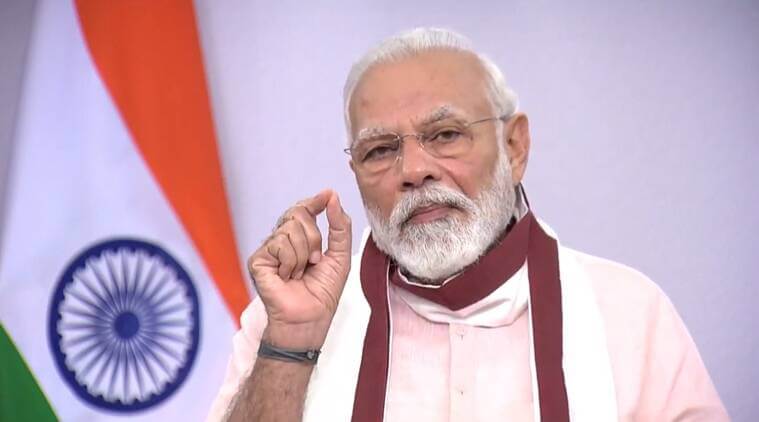

PM Narendra Modi issued a warning against antibiotics during his final Mann Ki Baat speech of the year on Sunday, December 28, 2025. Regarding public health, Modi brought up issues brought up in a recent report by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), which cautioned that antibiotics are losing their ability to treat illnesses like pneumonia and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
He warned that indiscriminate use of antibiotics was reducing their efficacy and recommended that people avoid using them without first consulting a doctor. He called for increased awareness and appropriate behaviour, saying that "misuse of antibiotics can make even small infections difficult to treat in the future."
Why antibiotic resistance is a growing concern in India
In India, antibiotic resistance is emerging as one of the major public health problems of the country. As reported in the latest studies conducted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), usual antibiotics are slowly losing their effectiveness to fight infections like pneumonia and urinary tract infections. This means illnesses that were once easy to treat are now taking longer to heal and, in some cases, becoming life-threatening.
What causes antibiotic resistance
According to Dr Sudha Vinod Menon, Director - Internal Medicine, Fortis Hospital, Bannerghatta Road, Bengaluru, antibiotic resistance is primarily caused by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics. There are numerous instances when people take
antibiotics without proper guidance from a doctor, discontinue the treatment halfway once they feel relieved, or take the leftover medications for minor illnesses such as colds and sore throats, which are usually viral and do not need antibiotics at all.
antibiotics without proper guidance from a doctor, discontinue the treatment halfway once they feel relieved, or take the leftover medications for minor illnesses such as colds and sore throats, which are usually viral and do not need antibiotics at all.
This misuse creates a situation where the bacteria survive, adapt, and become more resistant, thus making it very difficult to treat future infections.
What happens when antibiotics stop working
When antibiotics become ineffective, even minor infections can turn serious. Patients may need to take stronger doses of medications, longer hospital stays, or undergo intravenous treatment, which would lead to increased health risks and costs associated with treatment. Antibiotic resistance also puts vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and people with low immunity at higher risk. Patients should always keep in mind that antibiotics are to be taken only when prescribed by a qualified doctor and exactly as advised. It is also important to complete the full course, even if the symptoms improve; it is essential to fully eliminate harmful bacteria. Self-medication and pressuring doctors to prescribe antibiotics must also be avoided.
Public awareness, responsible use of medicines, and stronger infection control practices are the factors that can help slow down the development of antibiotic resistance. If immediate action is not taken, common infections that are treatable today may become major health threats in the future.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Health
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Should there be an India-Pakistan cricket match or not?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2026 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.






















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


