Junk food alone won't kill you, but doctor warns of hidden gut risks
Fri 26 Dec 2025, 01:35:42
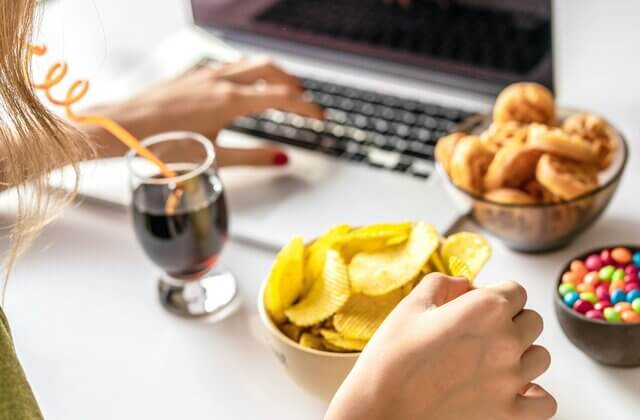

A deeply saddening case from Amroha, Uttar Pradesh, where 16-year-old Ahana died after a severe intestinal complication, has ignited conversations and some misinformation about junk food and gut health. According to multiple hospital reports and family accounts, her prolonged dislike for home-cooked meals and frequent consumption of fast and processed foods like pizza, burgers, chowmein and Maggi coincided with months of abdominal pain and deteriorating health before she was admitted to All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi, for advanced treatment.
Medical records shared with media indicate she suffered intestinal perforation, adhesions and widespread infection, conditions that overwhelmed her body despite surgical interventions. Some social media posts imply she “died from eating pizza and Maggi,” but doctors and nutrition researchers caution this oversimplifies the medical reality.
SEPARATING MYTH FROM MEDICINE
“It’s understandable for families to look for a reason,” says Dr Meera Gupta, Consultant Gastroenterologist, New Delhi.
“But there is no credible evidence that eating pizza or instant noodles once in a while directly perforates the intestines. What we do see scientifically is that diets chronically low in fiber and high in ultra-processed ingredients can disrupt gut balance, promote inflammation, and increase risks for conditions like gastritis, functional bowel disorders and nutrient deficiency over time.”
According to experts in gastrointestinal research:
. Ultra-processed foods high in emulsifiers and preservatives can alter gut microbiota and increase inflammation.
. Fast food consumption is associated with higher rates of functional gastrointestinal disorders in adolescents compared to peers eating less processed
diets.
diets.
. Chronic poor diets often lack fiber, which is essential for healthy intestinal movement and microbial balance.
“When we talk about junk food risks, we should be clear. Poor diet doesn’t directly cause a hole in the intestines. What it can do over months and years is weaken gut defenses, slow motility, and predispose to chronic inflammation and infection when other factors like infections, stress or medical conditions occur,” says Dr Gupta
She emphasised that foodborne illnesses or severe infections can lead to intestinal perforation, and dietary negligence may worsen recovery, but attributing a sudden death solely to eating particular foods like pizza or Maggi isn’t supported by clinical evidence.
REAL RISKS OF AN UNHEALTHY DIET
Though the direct cause of Ahana’s intestinal damage may be medically complex, researchers agree there are clear harms associated with habitual ultra-processed food consumption:
Gut microbiome imbalance leading to dysbiosis and inflammation.
Increased risk of functional gastrointestinal disorders including bloating, constipation and IBS.
Potential long-term elevations in risk for chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
ADVICE FOR PARENTS AND TEENS
Experts recommend:
. Increase dietary fiber: Vegetables, fruits, whole grains support gut motility and beneficial bacteria.
. Limit ultra-processed foods: Not because they “are deadly,” but due to their low nutrient content and potential to displace healthier choices.
. Stay hydrated: Dehydration worsens constipation and digestive discomfort.
. Seek medical care early: Persistent abdominal pain or digestive changes deserve professional evaluation.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Health
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Is it right to exclude Bangladesh from the T20 World Cup?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2026 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.
























.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


